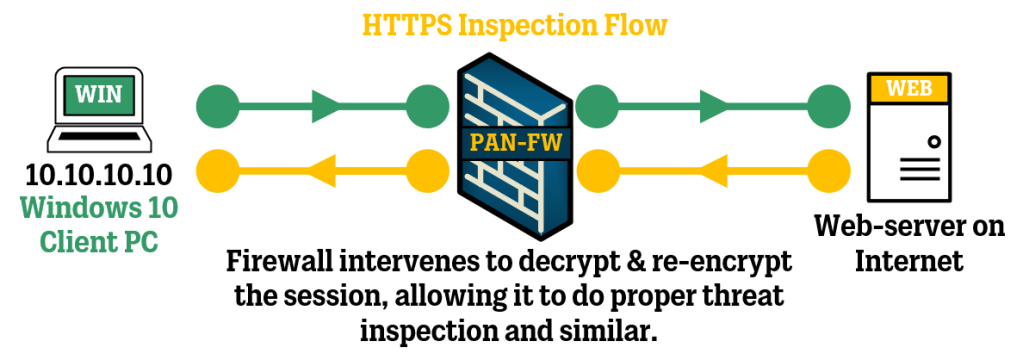
HTTPS protects web traffic with encryption; however, it also introduces risk as attackers may try utilizing the encryption aspect to get around your network’s defenses.
Even when connecting to a trusted source and establishing a secure SSL session, the accessed resource may host a virus or other malicious software. Without any further inspection, these threats may be cloaked by the encryption provided by SSL, pass through your defenses undetected, and end up in your network and on your devices!

SSL inspection is a technique used to inspect encrypted traffic. Two common methods include:
Certificate Inspection is used only with web filtering. It looks at the SSL/TLS handshake and verifies the identity of a web server.
Deep Inspection is used with all types of security scanning. It will decrypt incoming traffic to inspect and, if safe, re-encrypts and sends it to the recipient. Deep inspection also protects against attacks leveraging other secure protocols such as SMTPS, POP3S, IMAPS, and FTPS.
SSL Inspection methods may give rise to certificate warnings as your intermediary security device re-encrypts traffic with a self-signed certificate – appearing as a MitM attack.
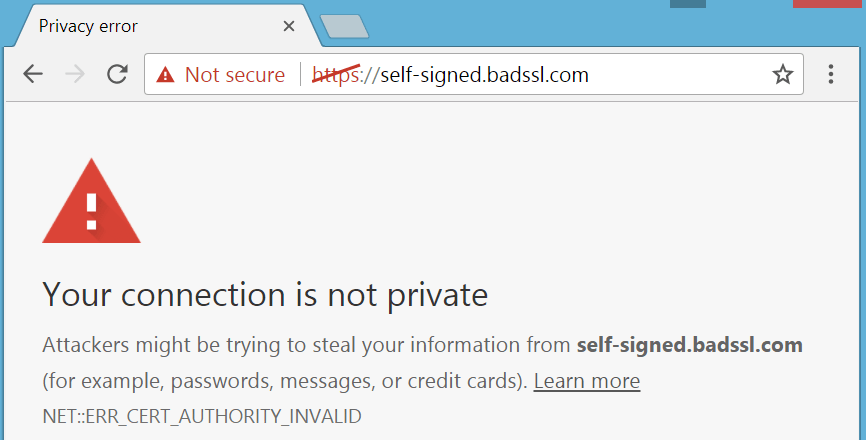
To avoid this: Download and install your vendor’s CA_SSL certificate on all workstations as a trusted root authority or Use a CA-Issued SSL certificate.
A more in-depth article on SSL Inspection can be found here.
~ G.G. May 2024




Leave a comment